1.3 Summarize the types of cables and connectors and explain which is the appropriate type for a solution.
Cable & Connector Types
-
Copper
- EMI - electromagnetic interference
- due to the nature of an electrical signal traveling down a metal wire it is vulnerable to EMI
- very strong source of power
- very strong radio source
- anything magnetic
- due to the nature of an electrical signal traveling down a metal wire it is vulnerable to EMI
- STP - shielded twisted pair
- shielded copper
- metal braided mesh wrapped around the internal core wire
- shielded copper
- UTP - Unshielded twisted pair
- less expensive
- lower transmission capabilities
- Twisted pair
- Cat 3
- Shielded
- no
- Max Transmission
- 10 Mbps
- Max Distance
- 100m
- Max Bandwidth
- 16 MHz
- Shielded
- Cat 5
- Shielded
- no
- Max Transmission
- 100 Mbps
- Max Distance
- 100m
- Max Bandwidth
- 100 MHz
- Shielded
- Cat 5e
- Shielded
- no/light shielding
- Max Transmission
- 1 Gbps
- Max Distance
- 100m
- Max Bandwidth
- 100 MHz
- Shielded
- Cat 6
- Shielded
- Both options are available
- Max Transmission
- 1 Gbps
- Max Distance
- 100m
- Max Bandwidth
- 250 MHz
- Shielded
- Cat 6a
- Shielded
- yes
- Max Transmission
- 10 Gbps
- Max Distance
- 100m
- Max Bandwidth
- 500 MHz
- Shielded
- Cat 7
- Shielded
- yes
- Max Transmission
- 10 Gbps
- Max Distance
- 100m
- Max Bandwidth
- 600 MHz
- Shielded
- Cat 7a
- Shielded
- yes
- Max Transmission
- 10 Gbps
- Max Distance
- 100m
- Max Bandwidth
- 1000 MHz
- Shielded
- Cat 8
- Shielded
- yes
- Max Transmission
- 25 Gbps/40 Gbps
- Max Distance
- 30m
- Max Bandwidth
- 2000 Mhz
- Shielded
- Cat 3
- Coaxial/RG-6
- Twinaxial
- Termination standards
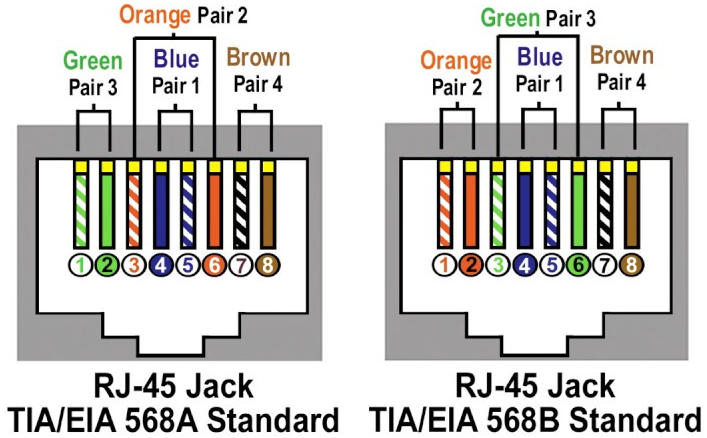
-
TIA/EIA-568A
-
TIA/EIA-568B
- EMI - electromagnetic interference
-
Fiber
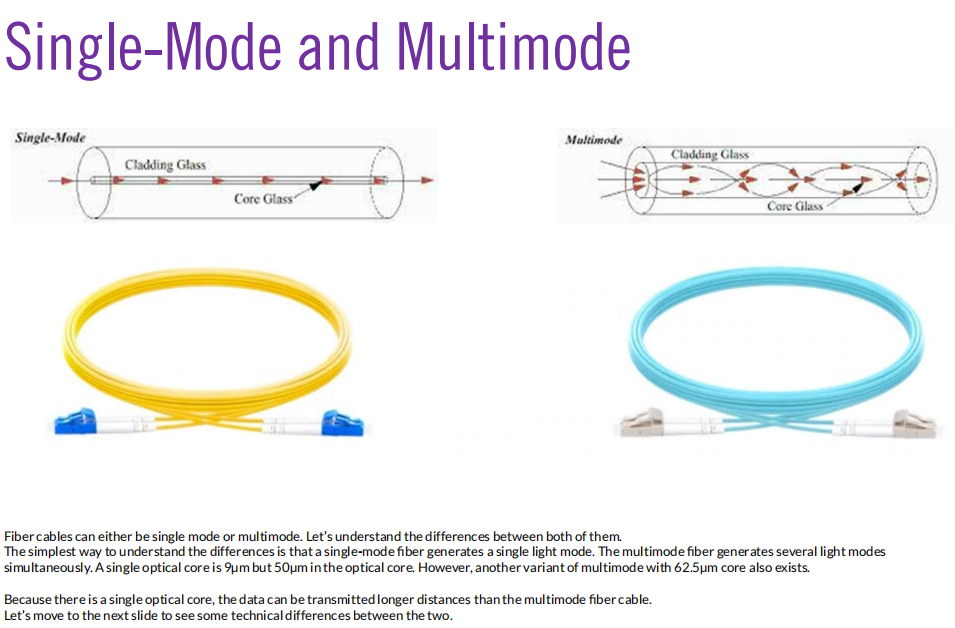
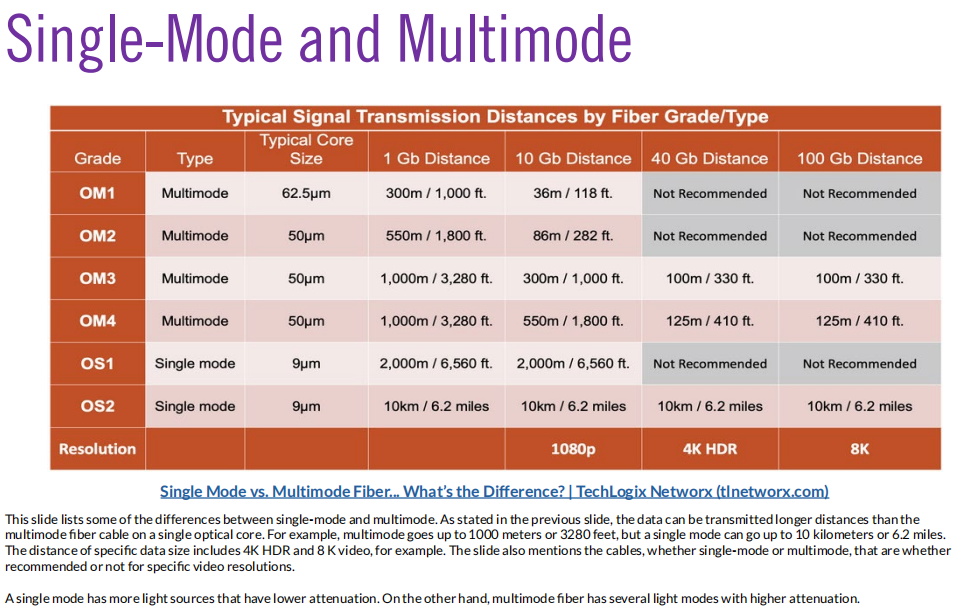
- Single-mode
- Multimode
-
Connector types
-
Local connector (LC)
-
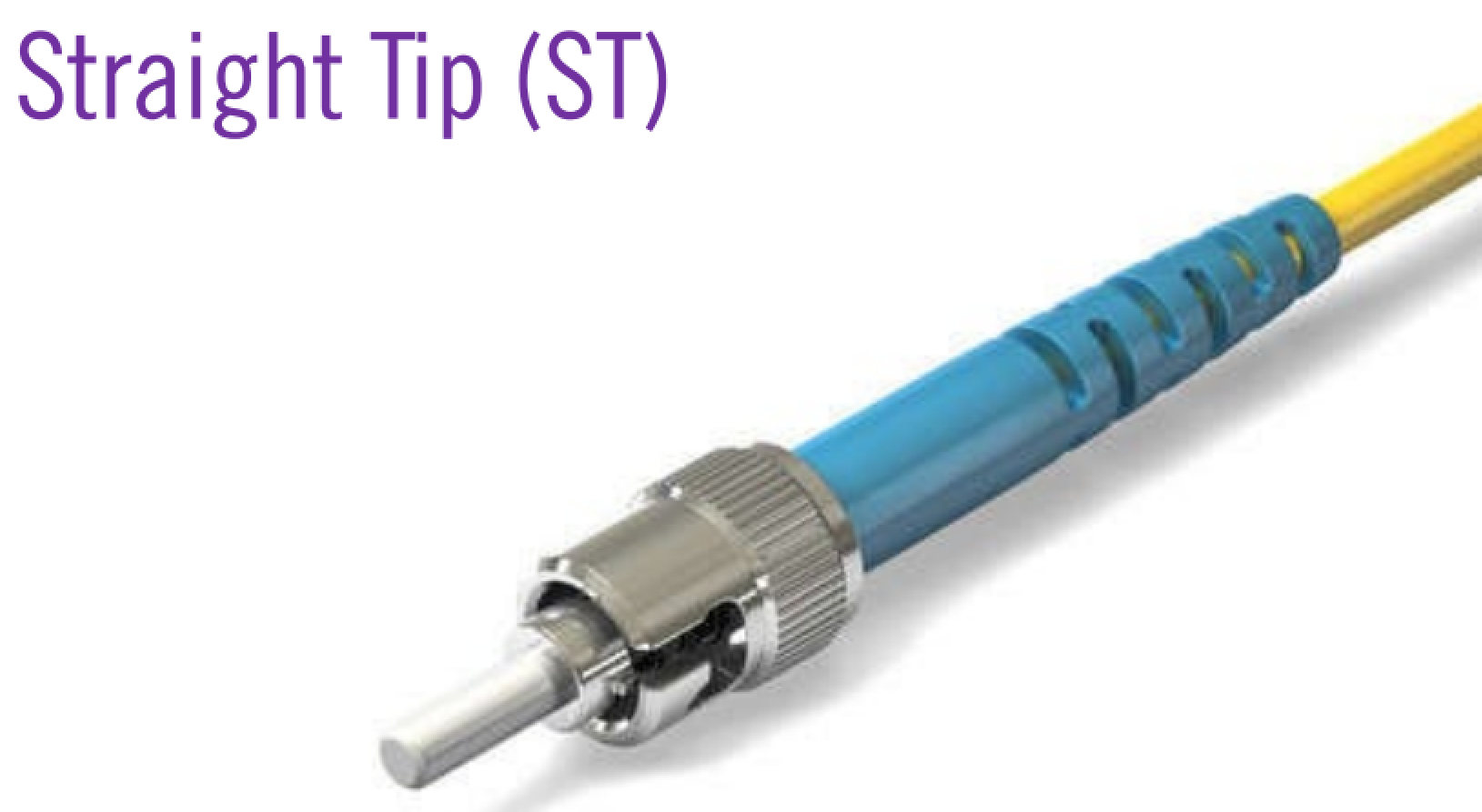
straight tip (ST)
-
subscriber connector (SC)
-
mechanical transfer (MT)
-
registered jack (RJ)
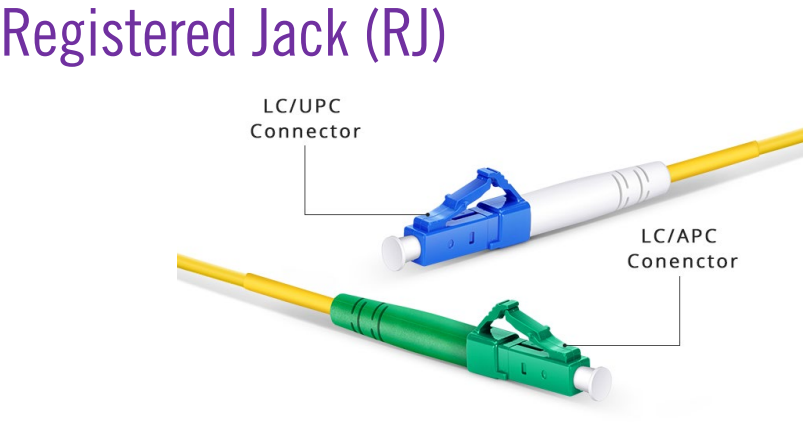
- Angled physical contact (APC)
- Ultra-physical contact (UPC)
-
RJ11
-
RJ45
-
F-type connector
-
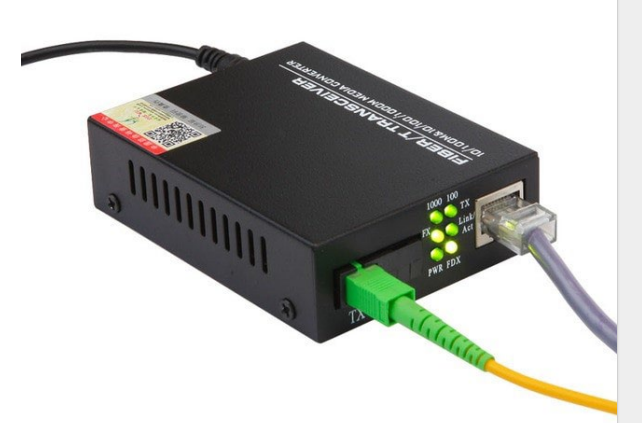
Transceiver/media converters
-
Transceiver type
- Small form-factor pluggable (SFP)
- Enhanced form-factor pluggable (SFP+)
- Quad small form-factor pluggable (QSFP)
- Enhanced quad small form-factor pluggable (QSFP+)
- Small form-factor pluggable (SFP)
-
-
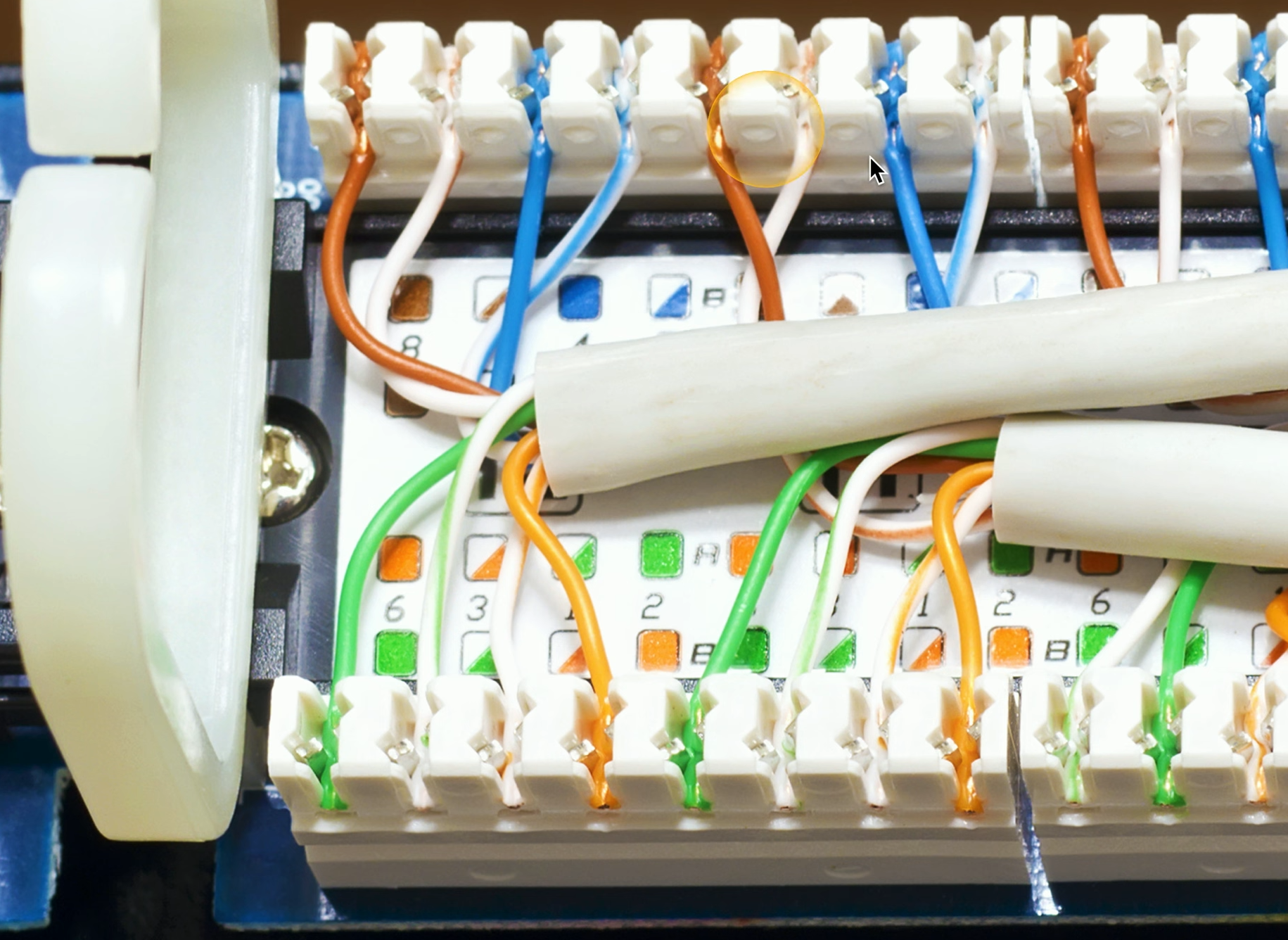
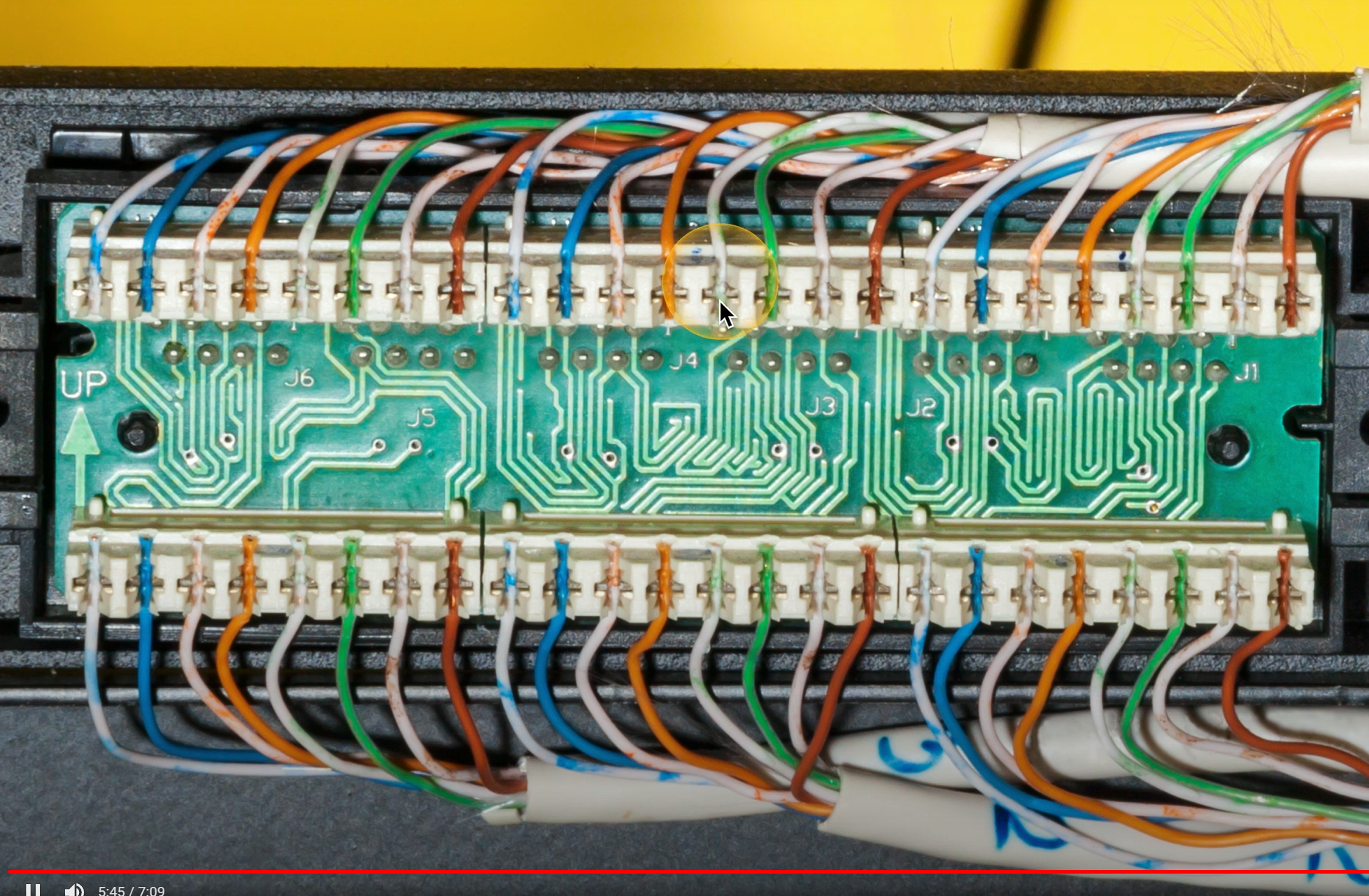
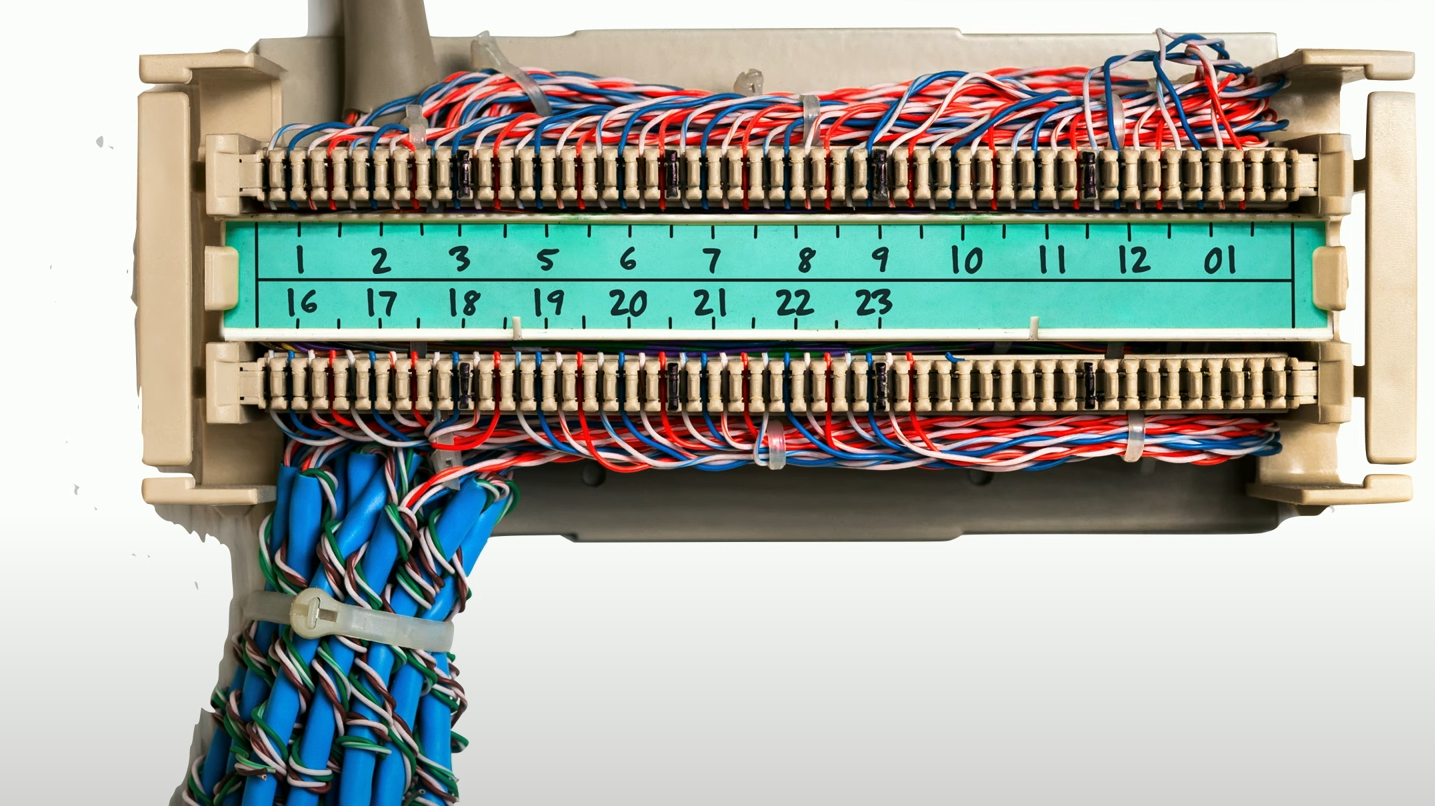
Cable management
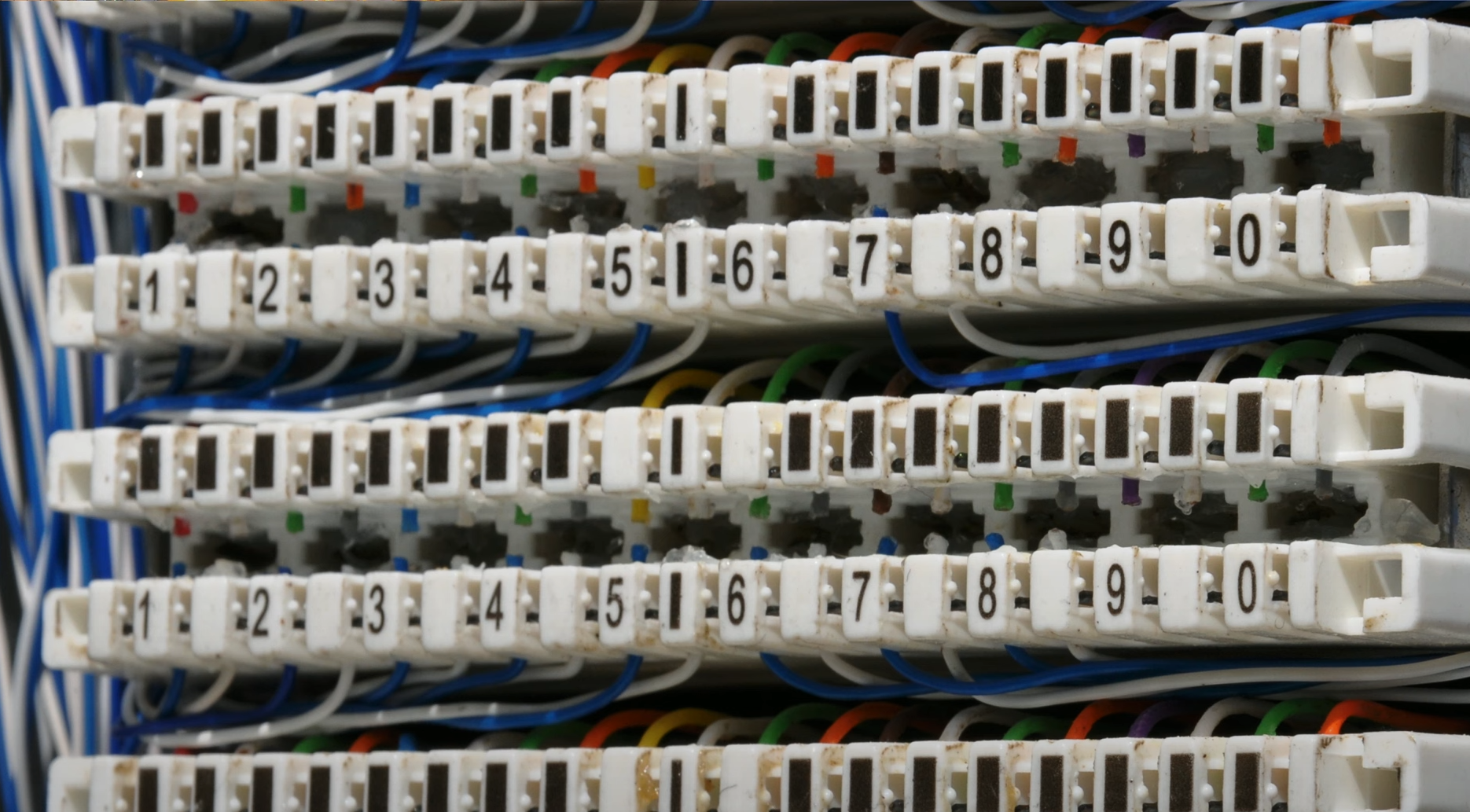
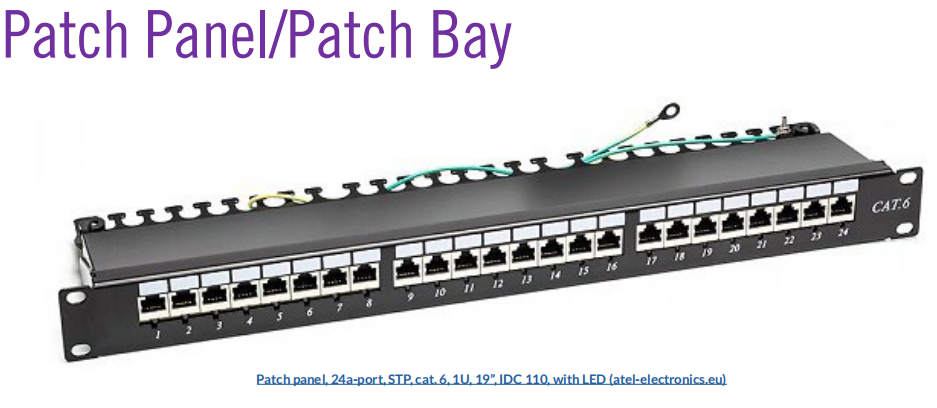
- Patch panel/patch bay
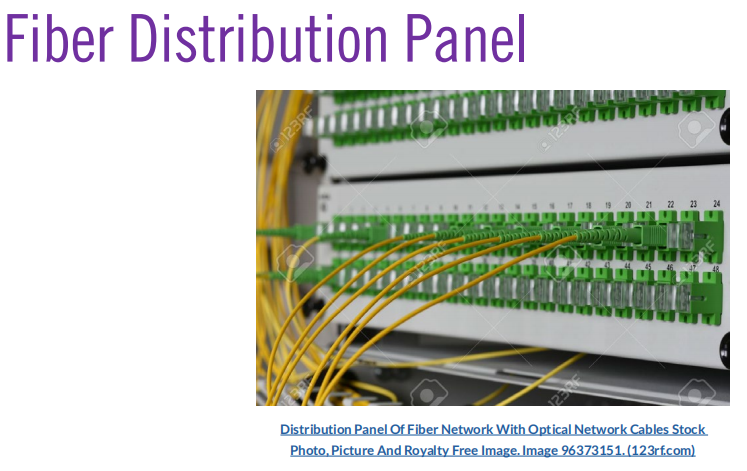
- Fiber distribution panel
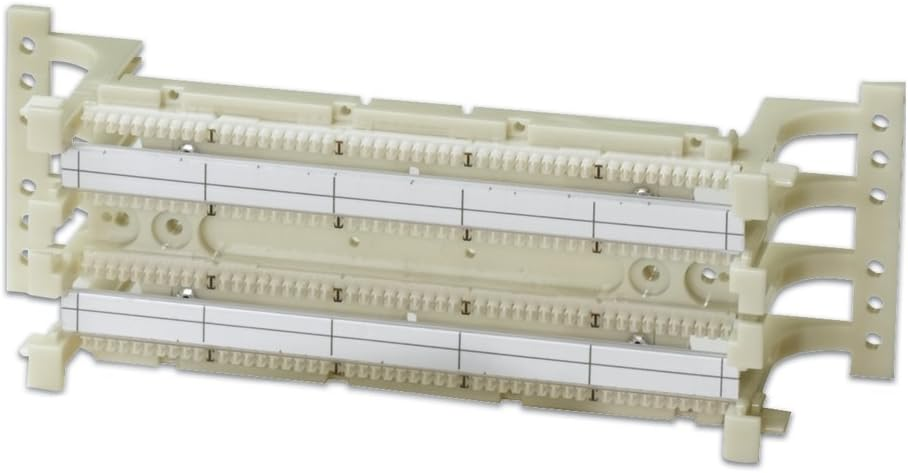
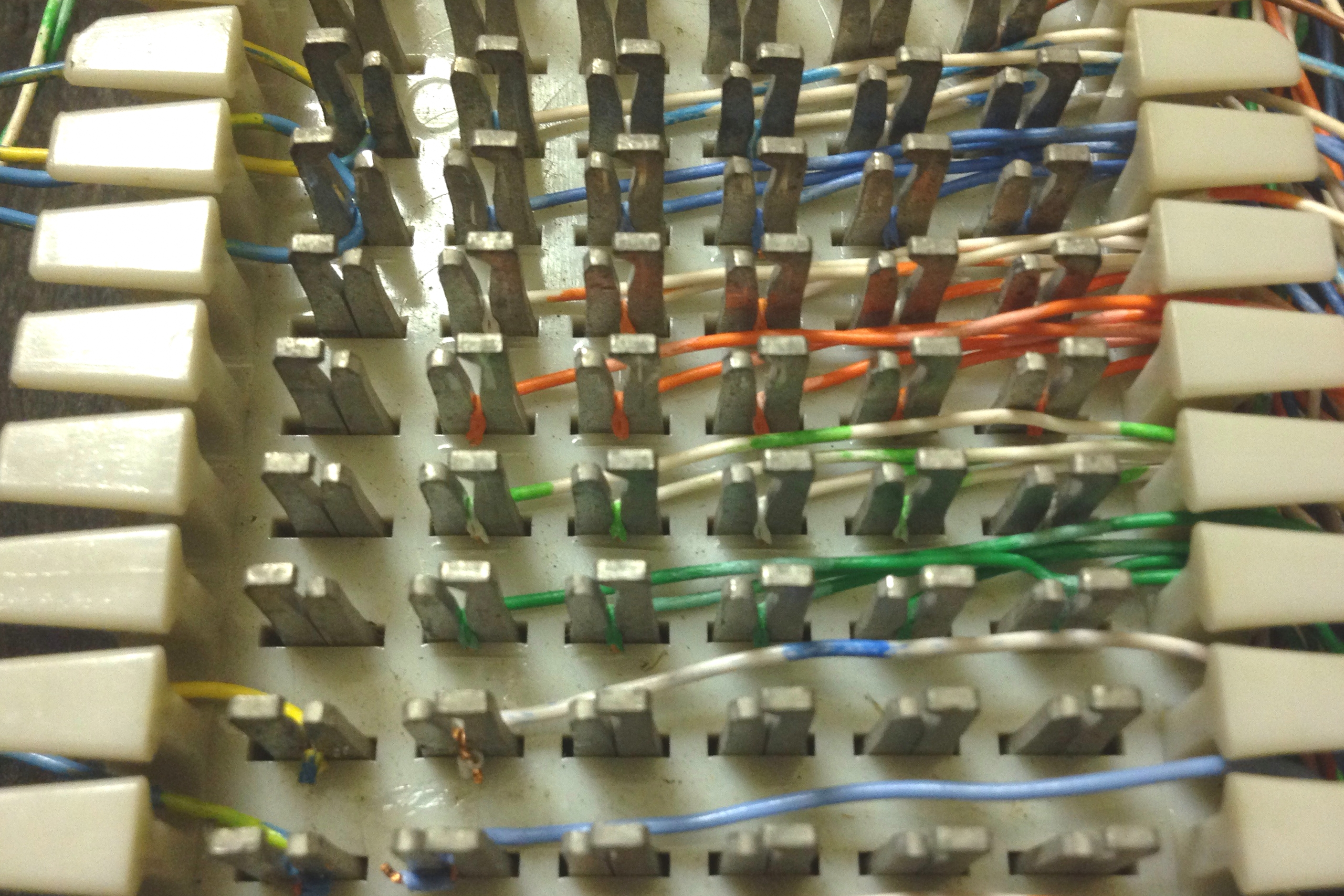
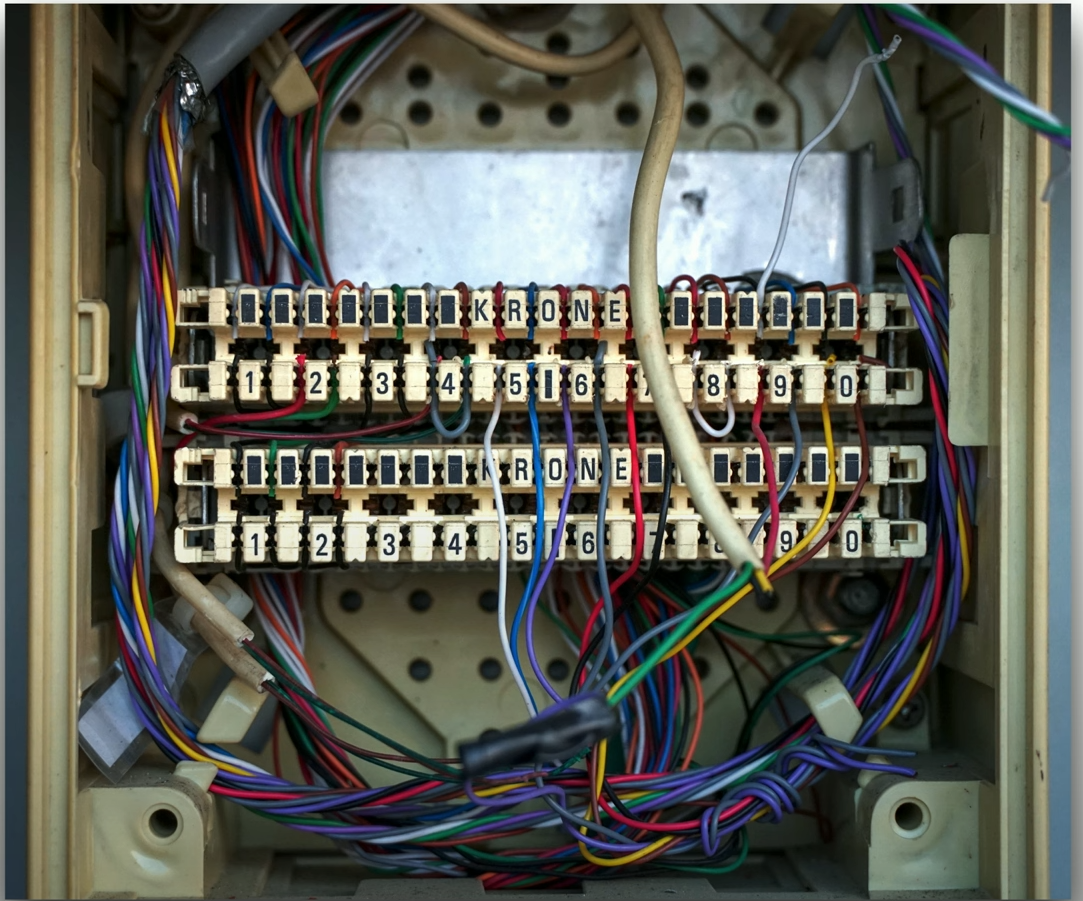
- Punchdown blocks
- 66 block
- 110 block
- Krone block
- Bix block
- 66 block
- Patch panel/patch bay
Ethernet Specifications
- Ethernet standards
- Copper
- 10BASE-T - 10 Megabit, Baseband over twisted pair cable
- two pairs of wire
- Cat 3 minimum
- 100 meter maximum distance
- 100BASE-TX - 100 Megabit, Baseband over twisted pair cable
- Fast Ethernet
- two pair
- Cat 5 minimum, twisted pair copper wires
- 100 meter maximum distance
- 1000BASE-T - Gigabit Ethernet over Cat 5
- 4 pair balanced twisted pair
- 125 Mhz
- Cat 5 is deprecated so we used Cat5e
- a shift to using all four pair of wires
- 100 meter maximum distance
- 10GBASE-T - 10 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- 4 pair balanced twisted pair
- 500Mhz
- requires minimum Cat 6
- Unshielded 55 meters
- shielded 100 meters
- Cat 6a (augmented)
- unshielded or shielded 100 meters
- 40GBASE-T - 40 Gigabit per second Ethernet
- 4 pair balanced twisted pair
- Cat 8
- up to 30 meters
- 10BASE-T - 10 Megabit, Baseband over twisted pair cable
- Copper
Fiber Optic Specifications
-
Fiber
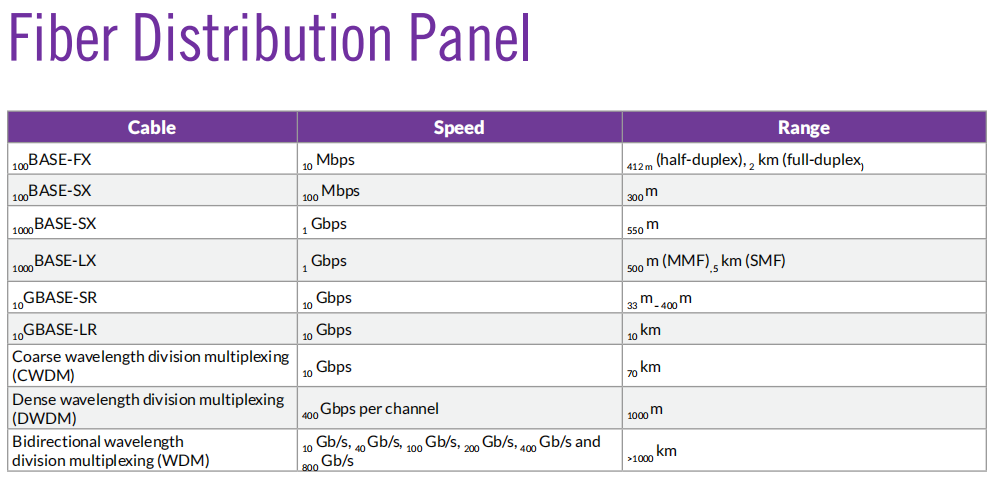
- 100BASE-FX - 100 megabit Ethernet over fiber
- pair of multimode fiber
- uses the same fiber as FDDI
- LED components
- 400 meters (half duplex)
- 2km (full duplex)
- 100BASE-SX - 100 megabit Ethernet over fiber
- a less expensive version of 100BASE-FX
- LED Optics
- 300 meters maximum distance
- 1000BASE-SX - Gigabit Ethernet using short wavelength laser
- Usually over multimode fiber
- 220 to 550 meters depending on fiber type
- 1000BASE-LX - Gigabit Ethernet using long wavelength laser
- Multimode fiber up to 550 meters
- single mode fiber up to 5km
- 10GBASE-SR - 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber, short range
- Multimode fiber
- 26 to 600 meters depending on fiber specification
- 10GBASE-LR - 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber, long range
- single mode fiber
- 10km maximum range
-
WDM - Wavelength Division Multiplexing
- Bidirectional communication over a single strand of fiber
- Use different wavelengths for each carrier
- Different “colours”
-
CWDM - Coarse wavelength division multiplexing
- 10GBASE-LX4 Used four 3.125 Gbit/sec carriers at four different wavelengths
-
DWDM - Dense wavelength division multiplexing
- Multiplex multiple OC carriers into a single fiber
- add 160 signals, increase to 1.6 Tbit/s
-
https://smartoptics.com/knowledgebank-post/cwdm-dwdm-explained/
Links to Videos and Additional reading
Professor Messer 1.2 – Network Topologies and Types
- Copper Cabling
- Optical Fiber
- Network Connectors
- Network Transceivers
- Cable Management
- Ethernet Standards
Back to the Central Hub