Overview
Python mind map
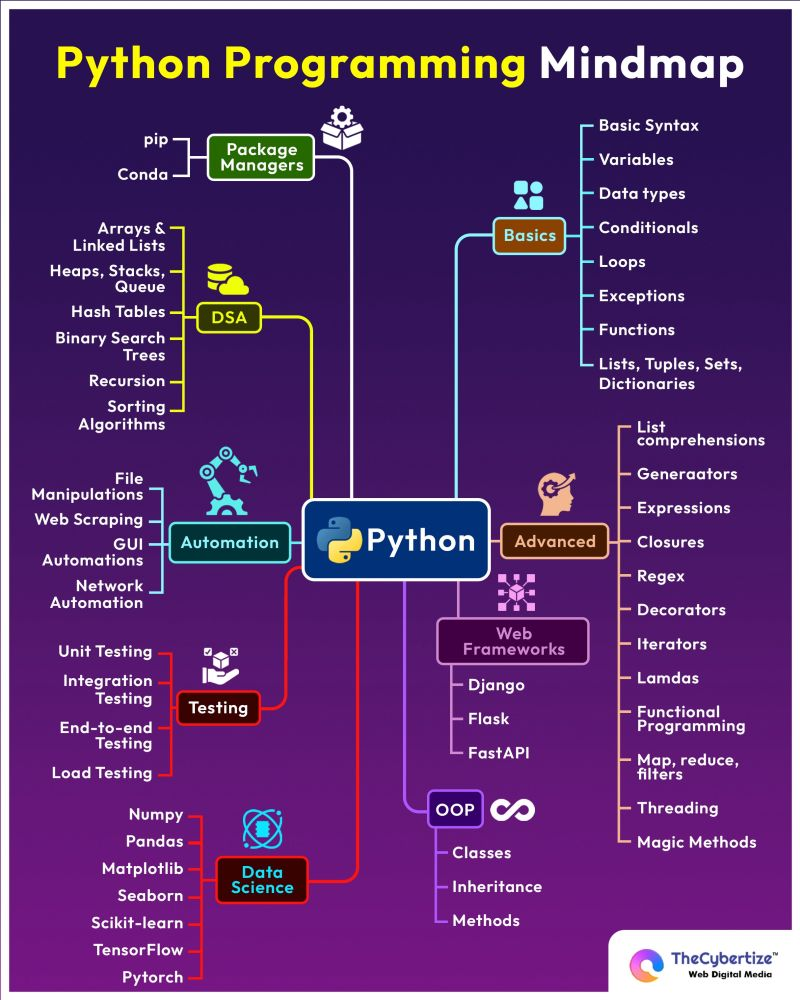
Lessons
Python Beginner Courses
- Programming with Mosh
- 📖 Table of Content
- 0:00:00 Introduction
- 0:00:56 What is Python?
- Most popular programming language
- used by Software engineers, Mathematicians, Data Analysts, Scientists, Accountants, Network Engineers, the list goes on.
- Ideal programming language to learn first, why is this?
- solve complex problems in less time with fewer lines of code
- example, we want to extract the first 3 characters from the string “Hello World”
C#-str.Substring(0,3)Javascript-str.substr(0,3)Python-str[0:3]
- example, we want to extract the first 3 characters from the string “Hello World”
- Python is a multi-purpose language and can be used for a large range of jobs
- Data Analysis
- AI/Machine Learning
- Automation scripts
- Web/Mobile/Desktop Apps
- Testing
- Hacking
- Python is a high level language
- don’t need to worry about complex tasks like memory management as seen in languages like
C++
- don’t need to worry about complex tasks like memory management as seen in languages like
- Cross Platform
- works on Windows, Linux and Mac
- Huge Community
- Large Ecosystem of libraries, Frameworks and tools
- Been around for over 20 Years
- solve complex problems in less time with fewer lines of code
- There are 2 versions of Python
- Python 2 which is supported up to 2020
- Python 3 which is Python for the future
- This Course covers Python 3
- 0:04:11 Installing Python
- installation media can be found at
- Python website
- from the front page click downloads and click the link for your operating system
- when installing ensure the box titled “add to path” is selected.
- On my system an older version of python was installed, the installer didn’t give me the option to “add to path” only an upgrade option. to ensure this is enabled on my system I followed the following steps
win+rtypesysdm.cpland press enter, go to advanced, environment variables, path, edit and add two new entry’s- Note: your name is the name of your user directory and python version is the latest release you upgraded to
C:\Users\<YourName>\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\<Python version>\C:\Users\<YourName>\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\<Python version>\Scripts\
- verify installation in command prompt with
python --versionpip --version
- from the front page click downloads and click the link for your operating system
- Python website
- installation media can be found at
- 0:05:36 Python Interpreter
- Python Interpreter
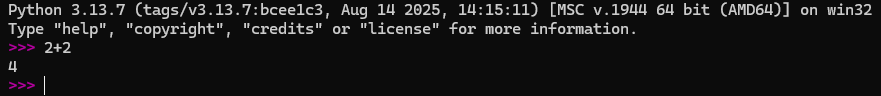
- By opening a shell and entering the text
pythonand typingenterwe are brought to the python interpreter which is basically a program that executes python code - We can type our code into a file and pass it to the interpreter or we type code directly into this interactive shell
- By opening a shell and entering the text
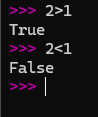
- Expressions
- An expression is a piece of code that produces a value
- Expressions can produce Boolean values as well which is similar to yes or no in English
- An expression is a piece of code that produces a value
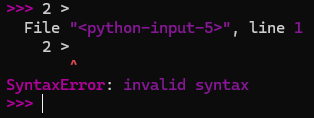
- Syntax errors are programming grammar errors
- Python Interpreter
- 0:07:30 Code Editors
- Two types of tools can be used to write python code
- Editor
- An editor is a program designed for writing and editing code, they are generally lighter and offer basic text editing.
- popular code editors
- VS Code - Visual Studio Code
- Atom
- Sublime
- IDE - Integrated Development Environment
- An IDE is a code editor with fancy features, such as:
- Autocompletion
- This helps you complete your code as you type, reducing the need to type every character by hand
- Debugging
- This feature helps in finding and fixing bugs (errors) in your programs
- Testing
- IDEs often include tools for writing and running tests for your code
- Linting
- This involves analysing your code for potential errors as you write it, providing immediate feedback (e.g. a red underline for invalid syntax
- Code Formatting
- Tools within an IDE can automatically format your code according to style guides like PEP 8, making it clean and readable
- Code Snippets
- These are reusable blocks of code that can be quickly generated
- Autocompletion
- Popular Python IDE’s Include
- PyCharm
- VS Code
- converted with an extension called ‘Python’ from Microsoft
- An IDE is a code editor with fancy features, such as:
- Editor
- Two types of tools can be used to write python code
- 0:08:49 Your First Python Program
- Project Setup in VS Code
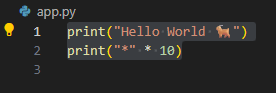
- First, you create a new folder on your disk, for example, named
hello world - Inside this folder, you create a new file, which for Python should always have the .py extension (e.g.,
app.py)
- First, you create a new folder on your disk, for example, named
- The
print()Function- Python includes many built-in functions for various tasks, similar to buttons on a TV remote
- function
print(), used to display content on the screen (console/terminal) - To use or “call” a function, you always follow its name with parentheses
() - When working with text (strings), you must enclose it in quotes (either double or single quotes). For example,
print("hello world")
- Executing Your Code
- After writing your Python code, you save the changes (e.g.,
Ctrl+Son Windows,Cmd+Son Mac) - VS Code has an integrated terminal (accessed by
Ctrl+Backtick) that allows you to execute your code without switching programs - To run your Python file, you type
python(on Windows) orpython3(on Mac/Linux) followed by the filename (e.g.,python app.pyorpython3 app.py) in the terminal
- After writing your Python code, you save the changes (e.g.,
- Code Execution Flow
- Instructions in your Python program are executed from top to bottom, in order
- Example
- Project Setup in VS Code
- 0:12:25 Python Extension
- The Python Extension turns VS Code into a powerful IDE for Python application development
- To install it, you navigate to the extensions panel in VS Code, search for “Python,” and install the official extension from Microsoft.
- The Python extension provides numerous functionalities, including:
- Linting
- Debugging
- Autocompletion
- Code Formatting
- Code Snippets
- Direct Code Execution
- 0:14:26 Linting Python Code
- This feature analyses your code for potential errors as you write it, preventing you from having to run the program to discover issues. It identifies problems such as missing parentheses in function calls (especially relevant for Python 3 vs. Python 2 code) or invalid syntax.
- The default linter used by the Python extension is Pylint, which is also the most popular choice among developers
- Other linters like flake8, mypy, and pep8 are also available and can be selected via the command palette
- This feature analyses your code for potential errors as you write it, preventing you from having to run the program to discover issues. It identifies problems such as missing parentheses in function calls (especially relevant for Python 3 vs. Python 2 code) or invalid syntax.
- 0:18:40 Formatting Python Code
- The extension provides tools to make your code clean and readable.
- It helps automatically format code according to PEP 8, which is a style guide defining rules for formatting Python code to ensure consistency.
- The extension uses autopep8 as the most popular tool for automatically formatting Python code.
- You can configure VS Code to automatically format your file every time you save changes by enabling the “Editor: Format On Save” setting.
- 0:22:51 Running Python Code
- 0:24:30 Python Implementations
- 0:26:59 How Python Code is Executed
- 0:29:45 Quiz
- 0:31:17 Python Mastery Course
- 0:31:44 Variables
- 0:34:48 Variable Names
- 0:37:51 Strings
- 0:43:20 Escape Sequences
- 0:46:01 Formatted Strings
- 0:48:09 String Methods
- 0:54:03 Numbers
- 0:56:50 Working With Numbers
- 0:58:59 Type Conversion
- 1:04:03 Quiz
- 1:06:43 Comparison Operators
- 1:08:46 Conditional Statements
- 1:12:56 Ternary Operator
- 1:15:04 Logical Operators
- 1:19:07 Short-circuit Evaluations
- 1:21:13 Chaining Comparison Operators
- 1:22:35 Quiz
- 1:24:18 For Loops
- 1:27:56 For..Else
- 1:30:42 Nested Loops
- 1:33:26 Iterables
- 1:36:34 While Loops
- 1:41:33 Infinite Loops
- 1:43:10 Exercise
- 1:45:13 Defining Functions
- 1:47:37 Arguments
- 1:49:57 Types of Functions
- 1:53:59 Keyword Arguments
- 1:55:59 Default Arguments
- 1:57:34 xargs
Back to the Central Hub